Aircraft Carrier Flight Path Angles
From the LSO NATOPS manual.
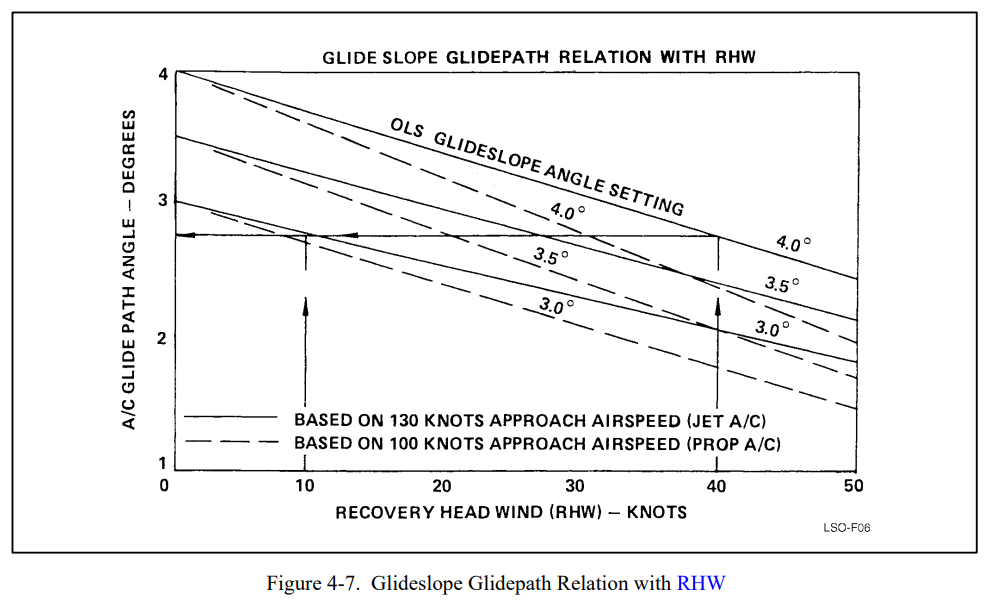
4.2.7 Effective Glideslope Due to Wind and Deck Motion
The glideslope angle, referred to as the basic angle aboard ship, is the fixed pitch angle around which the lens assembly stabilizes. A basic angle setting of 3.5° is most commonly used, with 4° used for higher wind-over-deck conditions (38+ knots) or on the small decks when hook-to-ramp clearance is near the 10-foot minimum. In moderate wind-over-deck conditions (32 to 37 knots), a 3.75° basic angle may be desirable. In Figure 4-7, note that decreased closure rate of aircraft to ship caused by wind-over-deck reduces the actual glideslope flown (effective glideslope).
| Wind Over Deck (kts) | Basic Angle (degrees) | Effective Glideslope* |
|---|---|---|
| 35 | 4 | 3.2 |
| 30 | 3.5 | 2.8 |
| *Based on a 130kt approach speed |
Calculating Effective Glideslope/Flight Path Angle
Given the glideslope angle (Basic Angle) of the meatball, the approach speed of the aircraft and the wind over the deck based on the aircraft carrier’s speed we need to calculate the flight path angle that the aircraft will follow, also known as the ‘effective glideslope’.
Some simple trigonometry.
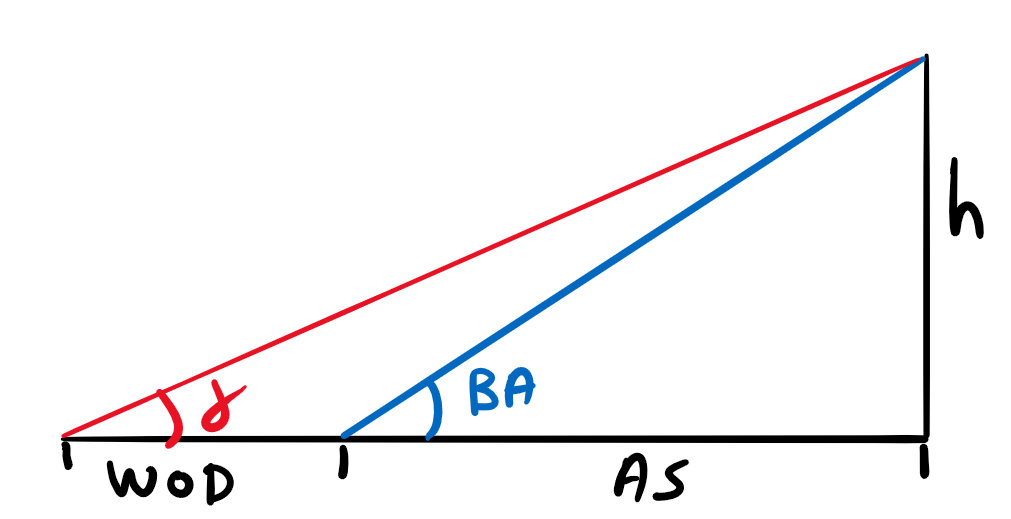
$$ h = AS tan(BA) $$
$$ \gamma = atan(\frac{h}{WOD + AS}) $$
Some code to implement the flight path angle calculation and to compare the results across different glide slope angles with varying amounts of wind over the deck.
def flightPathAngle(glideslope_angle, approach_speed, wind_over_deck):
h = approach_speed * math.tan(math.radians(glideslope_angle))
return math.degrees(math.atan(h / (wind_over_deck + approach_speed)))
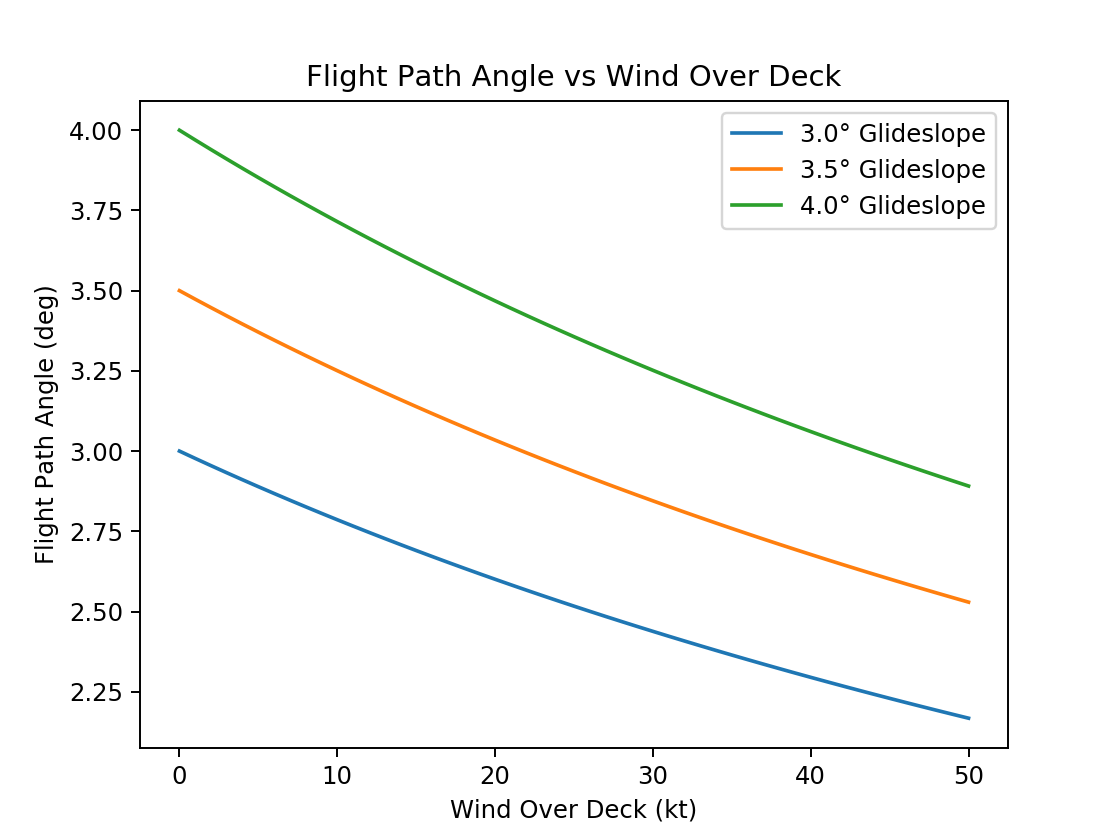
Generate a graph showing the change in flight path angle based on the wind over the deck for various glideslope angles for a specified approach speed.
approach_speed = 130
glide_slopes = [3.0, 3.5, 4.0]
for glide_slope in glide_slopes:
points = []
for wod in range(0, 51, 1):
points.append((wod, flightPathAngle(glide_slope, approach_speed, wod)))
wind_over_deck, gamma = zip(*points)
plt.plot(wind_over_deck, gamma, label=f'{glide_slope} Glideslope')
plt.xlabel('Wind Over Deck (kt)')
plt.ylabel('Flight Path Angle (deg)')
plt.legend()
plt.title('Flight Path Angle vs Wind Over Deck');
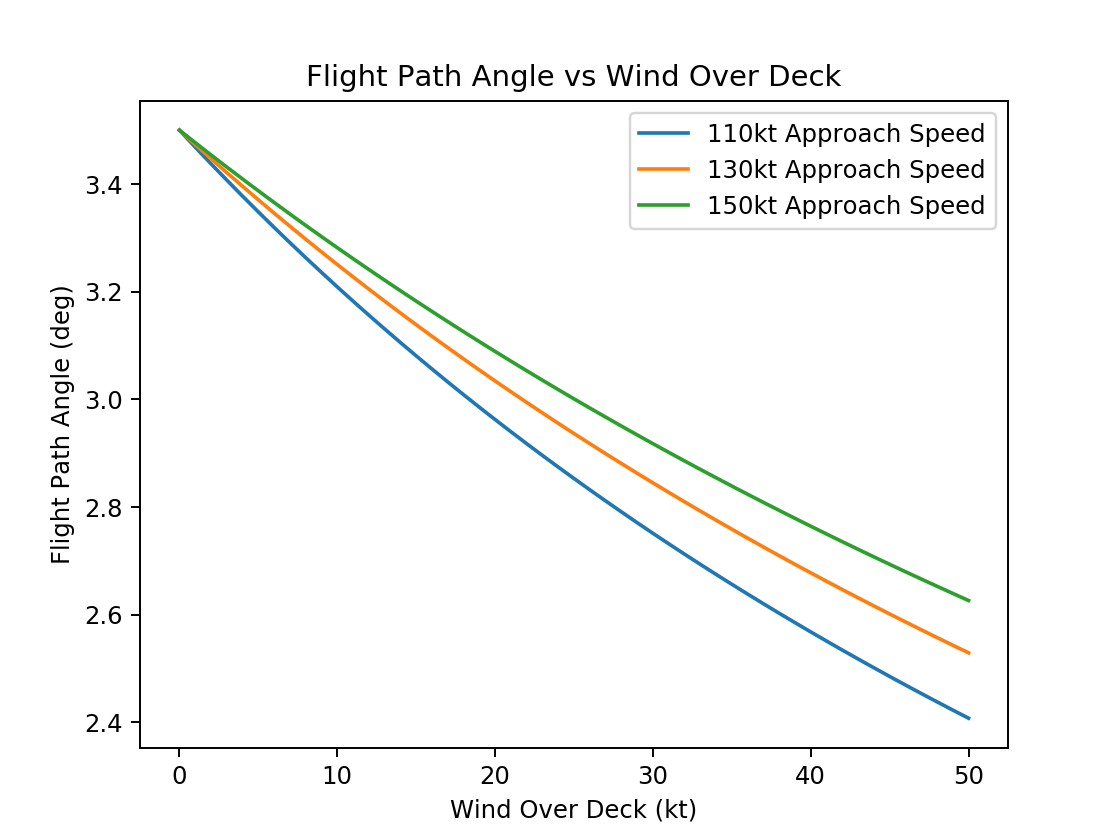
Now generate a graph showing the change in flight path angle based on varying approach speeds for a given glideslope angle.
approach_speeds = [110, 130, 150]
glide_slope = 3.5
for approach_speed in approach_speeds:
points = []
for wod in range(0, 51, 1):
points.append((wod, flightPathAngle(glide_slope, approach_speed, wod)))
wind_over_deck, gamma = zip(*points)
plt.plot(wind_over_deck, gamma, label=f'{approach_speed}kt Approach Speed')
plt.xlabel('Wind Over Deck (kt)')
plt.ylabel('Flight Path Angle (deg)')
plt.legend()
plt.title('Flight Path Angle vs Wind Over Deck');